How to Implement Effective Data Privacy Policies
In Business, Official BlogIn the modern world today, the privacy of data has remained a significant issue for most organizations globally. As more and more information is gathered, kept, and administered, the problems of protection become especially relevant. Jain which is an IT firm that deals with pioneering technology solutions for its customers highlighted the significance of sound data protection measures that would benefit the company as well as its clients. In the upcoming posts of this blog I will show you how to successfully put in place data privacy policies.
Understanding Data Privacy
Data privacy is slightly different from data security in that it deals with how data is managed and protected particularly personal, financial and health information. It concerns the regulation of factors related to the understanding of how information is amassed, processed, retrieved, and disseminated. Legal compliance means that the organizations meet the set laws on data privacy so that they do not compromise their customers’ and stakeholders’ confidence in the business.
Step 1: Undergo a Data Privacy Audit
The essential part of data privacy strategy is to carry out data privacy assessment initially. This involves:
Identifying Data Sources: Decide what sources your data comes from: websites, applications, customers, or third-party services.
Mapping Data Flows: Know the processes of data flow in the organization in order to identify how data is collected, where it is stored, processed and shared.
Classifying Data: Organize your data according to their level of sensitivity and relevance, thus, dividing it in personal data, financial data, health data and others.
These strategies imply that enhancing the obvious supervision and scrutiny can go a long way to facilitate data privacy by first exposing most of the potential vices and hence make it easier to contain them.
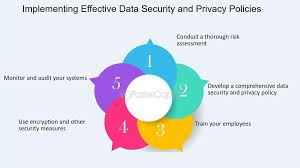
Step 2: Therefore, you should be familiar with regulations in order to know that you must not violate any laws or rules into the process of creating work and delivering it to the customer.
Specific legislation concerning data protection differs by country and these laws also differ according to a sector. One must familiarize wit
h the legal mandates that likely impact an organization.
Key regulations include:
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): Concerns organizations that provide goods and services to the EU citizens or are lo
cated in the EU countries.
California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA): Responsible for the safeguard of the privacy rights of people who reside in California.
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA): Governs the use of health information within the United States of America.
It is therefore important to seek legal advises concerning the kind of policies you intend to implement in the protection of your data.
Step 3: The previous activity was focused on creation of a Data Privacy Policy.
A data privacy policy is a type of business and organizational policy, which defines the company’s policy towards personal data.
Key components of an effective data privacy policy include:
Purpose and Scope: State why the policy is being formed and what data is to be regulated.
Data Collection: Analyze what data is gathered, how it is gathered and the necessity for it to be gathered.
Data Usage: Describe how data will be used, and to whom data will be accessible to.
Data Sharing: State instances where data will be shared with other third parties.
Data Security: Explain ways in which data privacy from access, breaches and leaks were implemented.
Data Retention: Decide on how long data will be stored and explicating methods of removing such data.
User Rights: Let the users know how their data can be processed and what rights they have including right of access, right to rectify and right to erasure.
Contact Information: Include the contact details of the company / organization for others to seek assistance on data issues.
Step 4: Use the following keys to enable data security:
Privacy and security in data are two sides of the same coin. One of the key components when doing any work involving sensitive data is to put into place the best security measures. Consider the following:
Encryption: Implement encryption as one of the techniques for protecting the data that is both in transit and at a standstill.
Access Controls: A, Control all accesses to the information so that only permitted personnel should be allowed to access the information.
Regular Audits: At least annual security check-ups should be performed in order to discover risks and threats, and respond to them properly.
Employee Training: Educate employees on proper handling and use of data, policies and measures to be followed in the company.
Incident Response Plan: Formulate strategies to deal with the possible data breaches and other security threats as soon as possible.
Step 5: In the may contain section, the guidelines state that in any manipulation of identified users, use of their personal data or extension of a current business relationship, the user’s prior consent has to be obtained.
User consent is one of the standard procedures used in the process of data privacy. Make sure the users are aware of data collection processes and allow them to give their consent on the same. Key practices include:
Clear Communication: It is essential to provide the general description of data collecting and using in simple words and lines.
Opt-In Mechanisms: Use options of obtaining user consent and conducting the collection of data only after such consent has been given.
Withdrawal of Consent: Easily enable users to withdraw their consent and respect their decision within the shortest time possible.
Step 6: Supervision and/or modification of the existing policies
Identity protection is in a continuous state. Make it your practice to review, as often as necessary, your data privacy policies to reflect regulatory solicitations, emergent tools, and threats.
Key steps include:
Regular Reviews: Make sure that you are conducting frequent checkups on your data privacy standard policies and procedures.
Stay Informed: In the case of data privacy, it is also significant to know updated laws and policies about the data protection.
Engage Stakeholders: Involve stakeholders which include legal consultants IT professionals and customers in the review process.
Step 7: Promote Privacy in the Organization
In developing such a culture of privacy, it is very important to sustain it in the long run within the organization. Ask the employees to be mindful of data protection with reference to their working routines.
Key initiatives include:
Training Programs: There should be and provide routine training for employees on the issue of data privacy.
Privacy Champions: Select private crusaders for departments to fight for data private.
Open Communication: Promote the freedom of discussing data privacy issues within the organization and allow the employees to report any suspicious activity.
Step 8: The following are the communication channels that exist in the different areas of the customers’ interface:
Honesty is the major component when it comes to dealing with customers. Make sure that the customers are well informed of the company’s data privacy standards and procedures.
Key practices include:
Privacy Notices: POST privacy notices on your website and at the point of collection.
User-Friendly Language: Therefore, following privacy policies and regulations one must ensure that the language used is easy for a common user to
understand.
Responsive Support: Provide adequate communication platforms through which the customers can seek more information about their data.
Step 9: Leverage Technology
Optimise data protection through the use of technology. Consider using tools and platforms that support data privacy initiatives:
Data Management Platforms: Embrace data management platforms as a mechanism of consolidating the data and its access.
Privacy Management Software: Use privacy management software to sweep the former compliance needs and allow users to consent.
Security Tools: Implement the higher-level security technologies like intrusion detection systems and data loss prevention solutions.
Step 10: What needs to be done is to measure and enhance this aspect to an optimal level.
Connect their data privacy policies and practices to a continuous improvement cycle. Utilize measures or evaluation to determine where exactly the organisation went wrong.
Key steps include:
Performance Metrics: These Include; Data breach counts, user complaints and compliance issues.
User Feedback: Gather the users’ response to design and product in order to assess the problematic areas.
Continuous Improvement: Apply the concept of constant improvements to try to make changes and improvements that would help increase the effectiveness of data privacy.
Conclusion
The establishment of proper data privacy measures are important to safeguard customer data and build the confidence of the consumer and the stockholder of the company. By doing so organizations can establish good policies concerning protection of data privacy which satisfies legal requirements and fosters good privacy culture. Unlike some of the other software development companies Jain Software strictly adhere to concept of data privacy and strives to provide organizations with guidelines to follow so as to incorporate the best practices in data protection and management.